We dive into the new Cosmos whitepaper and look into Chainlink after its recent rally.
1.Cosmos Hub
$ATOM is the Cosmos Hub’s primary token and secures the Hub’s interchain services through staking. In turn, stakers receive rewards & vote on governance.
New updates from the $ATOM 2.0 Whitepaper
- Instead of serving as a template for building blockchains into the Cosmos “interchain”, the role of Hub has been revamped as the heart of Interchain Security. Other chains can use the Hub to secure their networks, and validators will be rewarded with its revenue.
- Changes in the utility and issuance schedule of $ATOM:
- The purpose of $ATOM changes from providing security for the Cosmos Hub to value accrual by putting $ATOM at the core to secure a wider swath of the ecosystem via interchain security and liquid staking.
- A two-step new monetary policy for $ATOM will eventually bring down $ATOM’s inflation rate to 0.1% over the medium term.
Source: Map of Zones
Token: $ATOM

Source: Greythorn Research Team, Data: CoinGecko, DefiLlama
Comparables

Source: Greythorn Research Team, Data: CoinMarketCap
Bullish Fundamentals:
- Cosmos has a well-developed infrastructure and provides a development framework, Cosmos SDK, which allows developers to develop a customised chain in 15 minutes. 262 applications & services are built on the Cosmos ecosystem.
- Cosmos is relatively independent. It can autonomously decide the functions & governance model of the chain. It also has significant cross-chain freedom as opposed to slot auctions like Polkadot.
- The Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol was launched in April 2021, allowing applications to communicate with each other.
- $ATOM will be gradually empowered with more functions, i.e. for use as gas fees, staking and voting.
- Interchain Security allows smaller chains to ‘rent security’ from the Hub. This function is set to be available from January 2023. Cosmos contributors have proposed spending 150,000 ATOM tokens (~$1.1m) from the official Cosmos Hub community pool to attract projects that use interchain security.
Bearish Fundamentals:
- $ATOM is currently an inflationary token with an annual diluted inflation rate of 12.86% and an estimated reward rate of 17.97%. The real yield amounts to only ~5%, slightly higher than US treasuries.
- Since zones are using their tokens for verifications and gas fees, $ATOM currently has a weak ability to capture value despite the increased activity in these zones. Alternatives such as Osmosis (Liquid Centre), Evmos (EVM Centre), Juno (WASM Centre) and Axelar Network (non-IBC) are displaying notable growth.
- Few projects launch their mainnet without any native stablecoin support. Cosmos is one of them.
2. Chainlink
Chainlink is a decentralised network of oracles designed to securely and reliably connect blockchain smart contracts and off-chain computation. Being compatible with a wide range of blockchains on the EVM & Solana, users can filter oracles and customise the terms of service with a high degree of flexibility.
$LINK is the native token of Chainlink:
- Users purchase services from nodes with $LINK.
- Node operators will use $LINK as margin to assure the quality of their services. (Staking & future fee opportunities are utilised to correct nodes’ behaviour)
- Nodes with higher margin are more likely to be selected to provide services and earn $LINK.
- The margin of problematic nodes may be collected by Chainlink as a punishment for providing poor-quality service. The super-linear staking & watchdog mechanisms considerably increase the cost of any potential bribing schemes.
* Implicit-Incentive Framework (IIF) can be seen as parameterisation of the staking system, which reflects node incentives with greater accuracy.
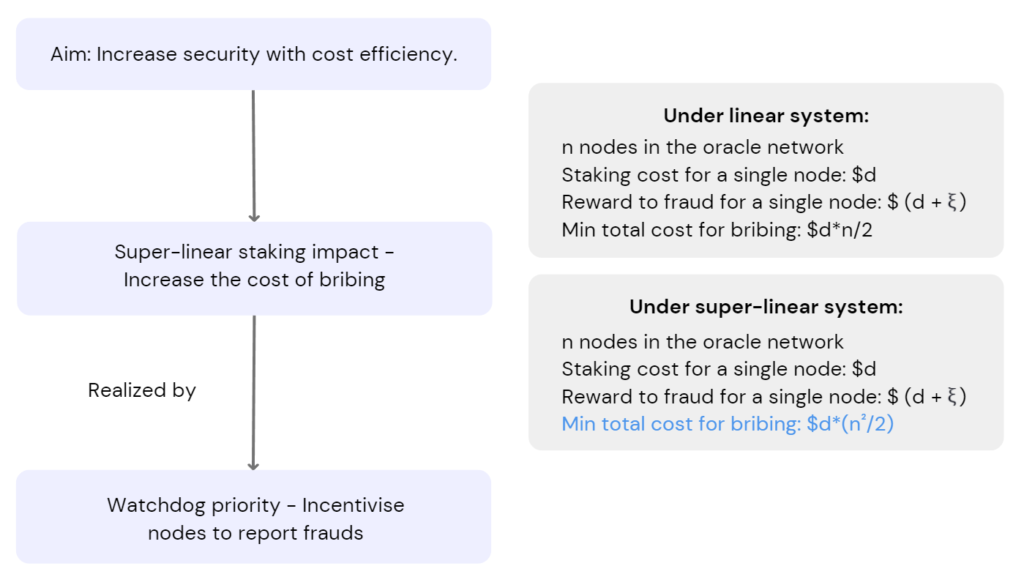
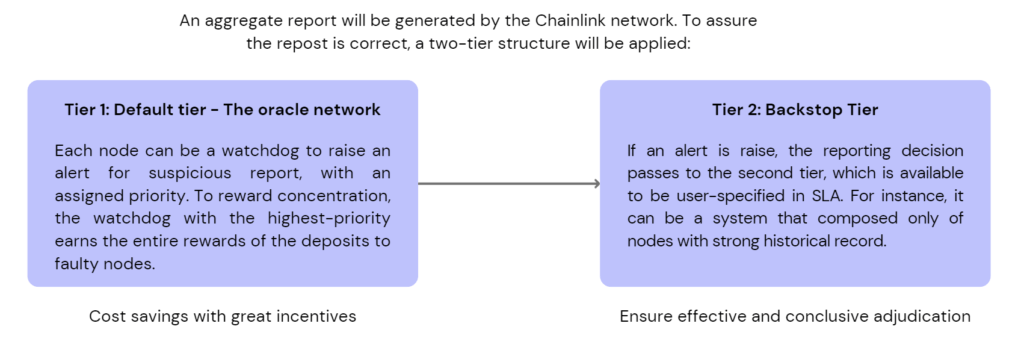
Source: Greythorn Research Team, Data: Chainlink Whitepaper
Token: $LINK
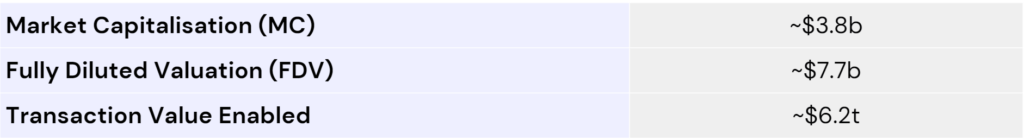
Source: Greythorn Research Team, Data: CoinGecko, Chainlink
Comparables

Source: Greythorn Research Team, Data: CoinMarketCap
Bullish Fundamentals:
- Incentive & Safety mechanism for Oracle nodes: Nodes can enjoy an ongoing revenue stream from users and future opportunities from their good behaviour. A virtuous cycle can be formed.
- Less supply pressure from the staking mechanism: To combat the immediate sell-off of $LINK when collecting rewards, oracle nodes have incentives to stake their token back to attract more users, allowing a growing ecosystem.
- Active Development: Chainlink is developing a range of products beyond oracles in its vision of becoming the main infrastructure layer for blockchain technology;
- VRF, Verifiable Random Function, to ensure the security of smart contracts by generating unpredictable outcomes,
- Keepers, also called Automation Documentation, enable conditional execution of smart contracts under specific incentives,
- DECO, an oracle scheme with a privacy protection function, and
- CCIP, a universal cross-chain communication protocol to transmit data and smart contract instructions.
An obvious first-mover advantage has been formed and will only strengthen with further development.
Bearish Fundamentals:
- The barrier for new oracles: Locked rewards and future fee opportunities (FFO) reinforce complete service delivery, requiring new oracles to stake large amounts of $LINK to be trusted and develop further.
- Considerable non-circulating supply: Non-circulating supply accounts for ~50% of $LINK’s token supply (23 addresses). Apart from Binance, the top 16 largest token holders are all of Chainlink’s non-circulating addresses set aside for rewards & further development incentives.
Closing Remarks
Reducing imbalanced supply pressure is becoming a critical priority across DeFi, as Cosmos becomes the latest ecosystem to reduce inflationary rewards. Similarly, Chainlink incentivises nodes to re-stake their tokens & attract more users in a bid to improve the ecosystem’s sustainability.
References
Chain.link. 2022. Blockchain Oracles for Hybrid Smart Contracts | Chainlink. [online] Available at: <https://chain.link/> [Accessed 7 October 2022].
CoinGecko. 2022. Cryptocurrency Prices, Charts, and Crypto Market Cap | CoinGecko. [online] Available at: <https://www.coingecko.com/> [Accessed 10 October 2022].
CoinMarketCap. 2022. Cryptocurrency Prices, Charts And Market Capitalizations | CoinMarketCap. [online] Available at: <https://coinmarketcap.com/> [Accessed 10 October 2022].
Cosmos: The Internet of Blockchains. 2022. Cosmos: The Internet of Blockchains. [online] Available at: <https://cosmos.network/> [Accessed 7 October 2022].
DefiLlama. 2022. DefiLlama. [online] Available at: <https://defillama.com/> [Accessed 9 October 2022].
Mapofzones.com. 2022. Map of zones – Cosmos network explorer. [online] Available at: <https://mapofzones.com/home?columnKey=ibcVolume&period=24h> [Accessed 9 October 2022].




